The Spanish Red Cross, known locally as Creu Roja, has taken a historic step toward redefining humanitarian aid delivery by introducing a blockchain-based digital aid platform that prioritizes both transparency and privacy. In an era where humanitarian organizations face increasing pressure to prove accountability while safeguarding vulnerable populations, this initiative signals a powerful shift. The platform digitizes the entire aid lifecycle—from donation and verification to disbursement and spending—while ensuring that no personal or biometric data is exposed on public systems. This move positions the Red Cross at the forefront of ethical, technology-driven humanitarian innovation.
Red Cross’s Vision for Privacy-First Digital Aid

For decades, humanitarian aid systems have depended heavily on manual paperwork, physical vouchers, and prepaid cards. While functional, these methods are slow, expensive, and difficult to audit at scale. Even newer digital solutions have introduced their own risks by requiring sensitive personal information, often forcing beneficiaries to trade privacy for assistance.
Creu Roja’s vision challenges this compromise entirely. The organization set out to build a system where individuals in need could receive support without being tracked, profiled, or exposed to long-term digital risks. By partnering with Barcelona-based technical infrastructure company BLOOCK, the Red Cross ensured that privacy was not an afterthought, but the foundation of the system’s architecture. Even if external systems were compromised, the blockchain layer itself would reveal nothing exploitable about recipients.
How the Blockchain-Based Aid Platform Works
At its core, the platform integrates existing enterprise IT systems with blockchain infrastructure in a way that feels invisible to beneficiaries. Ethereum was chosen as the public blockchain layer, while Solidity-based smart contracts manage the issuance of ERC-20 digital aid credits.
Recipients receive these credits directly into personal mobile wallets developed using Ionic technology. There is no need for a bank account, credit history, or formal financial documentation. Once issued, the credits can be spent at authorized local merchants by scanning a QR code. From the merchant’s perspective, the transaction looks exactly like any regular digital payment—there is no label, flag, or marker identifying it as humanitarian aid.
This design not only reduces stigma but also allows recipients to maintain dignity and normalcy in their daily transactions.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Advanced Data Protection
One of the most innovative aspects of the platform is its use of zero-knowledge proof technology, implemented through Billions Network (formerly Polygon ID). Zero-knowledge proofs allow the system to verify eligibility, authenticity, and transaction validity without revealing any underlying personal information.
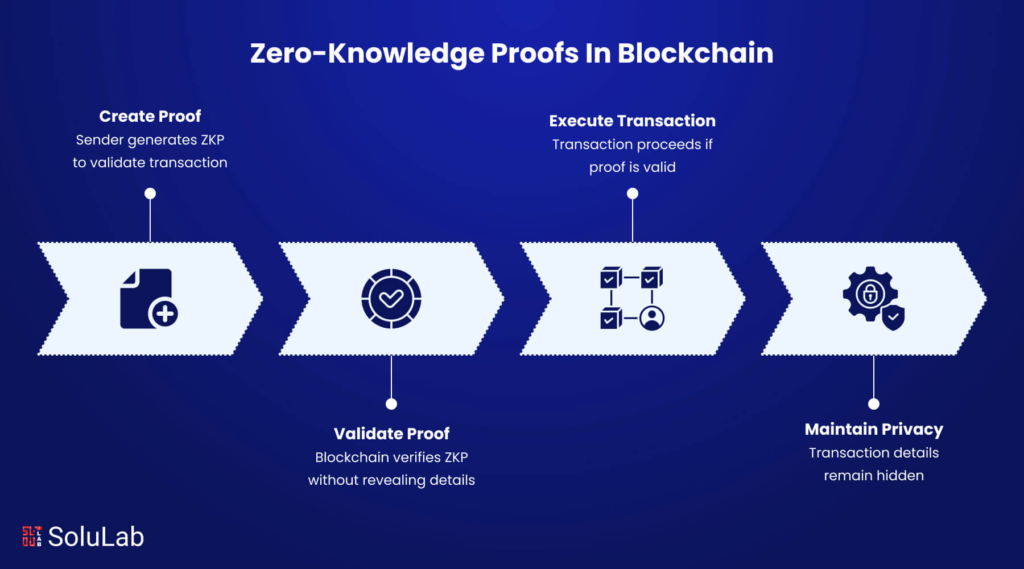
In practice, this means that recipient identities, case files, and sensitive data never touch the public blockchain. All such information remains securely stored off-chain within systems fully controlled by Creu Roja. The blockchain only records cryptographic hashes—mathematical proofs that confirm actions occurred correctly without exposing who was involved.
As a result, the platform achieves a rare balance: full auditability for donors and administrators, combined with complete privacy for beneficiaries.
Donor Transparency Without Surveillance
Transparency is essential for maintaining trust in humanitarian aid, especially as donors increasingly demand proof of impact. This platform addresses that demand by enabling real-time visibility into aggregated aid flows. Donors and administrators can see how much aid has been allocated, how much has been spent, and where funds are being used geographically.
Importantly, this transparency is structural, not invasive. Donors never gain access to individual identities, purchase histories, or personal circumstances. The system deliberately separates what donors need to know from what they do not, ensuring accountability without turning aid recipients into data points.
This approach redefines transparency as ethical visibility rather than total exposure.
Why This Platform Was Needed
The need for such a system has never been greater. International aid delivery has faced criticism due to corruption, inefficiency, favoritism, and lack of accountability. At the same time, many blockchain-based aid experiments have drawn backlash for relying on biometric databases and centralized identity systems.
Even well-intentioned technologies can unintentionally expose vulnerable populations to surveillance, discrimination, or misuse of personal data. Creu Roja recognized that humanitarian innovation must not introduce new risks under the guise of efficiency.
By using blockchain purely as a verification and certification layer—not as a data storage mechanism—the organization avoids these pitfalls while still benefiting from the technology’s strengths.
WMT Stock Soars Today as Walmart Shares Rally
Walmart Inc. (NYSE: WMT) continues to attract massive attention from investors as its stock price…
Best Alphabet’s Massive 2026 AI Spending Stuns Wall Street
Alphabet Goes All-In on Artificial Intelligence Alphabet Inc., the parent company of Google, has unveiled a massive…
Meta Shares Skyrocket as Company Reports Historic Sales Growth
Meta said its capital expenditures could nearly double to $135bn this year as part of…
Creative Confidence: Gerard Way’s Take on Business Growth
Growing a lifestyle business is a blend of passion, creativity, and smart strategy. Gerard Way—musician,…
Easy Guide to Buying Samsung Galaxy S25 from the US
The Samsung Galaxy S25 series is one of the most talked-about phone launches of the year, and many…
From Couture to Culture: Valentino’s Luxury Story
There are luxury fashion houses, and then there are names that feel like pure legacy….
What Industry Leaders Are Saying
Francisco López Romero, Chief Technology Officer at Creu Roja in Catalonia, emphasized that access to aid should never come at the cost of personal freedom or dignity. According to him, beneficiaries should not have to choose between getting help and protecting their privacy—a principle that guided every design decision of the platform.
Evin McMullen, CEO and co-founder of Billions Network, described the system as a credential-based model rather than a surveillance system. In this setup, recipients hold proof of eligibility in their own wallets, reveal only what is necessary, and retain full control over their identity.
BLOOCK CEO Lluís Llibre reinforced this philosophy by stating that blockchain’s role should be to certify truth, not to store content. Every transaction generates a cryptographic proof that is permanent and verifiable, yet completely free of personal data.
Technology Stack Behind the Platform
The platform is built on a robust and scalable technology stack designed for real-world humanitarian operations. Ethereum serves as the trusted public blockchain layer, while ERC-20 smart contracts enable standardized issuance of digital aid credits. Zero-knowledge proofs ensure privacy-preserving verification, and role-based access control combined with digital signatures secures system access.
The mobile wallet is built using Ionic, while Angular powers the administrative and merchant dashboards. A Go-based backend with REST APIs ties the system together, ensuring reliability and scalability. To date, the platform has processed more than 952,000 cryptographic transactions and over 257,000 data validations, demonstrating its operational maturity.
The Future of Humanitarian Aid

Creu Roja’s blockchain initiative represents more than a technological upgrade—it signals a philosophical shift in how aid should be delivered in the digital age. By proving that transparency and privacy are not mutually exclusive, the platform sets a powerful precedent for humanitarian organizations worldwide.
As governments, NGOs, and public-interest institutions explore digital identity and blockchain solutions, this model offers a clear lesson: technology should empower people, not expose them. The Red Cross has shown that it is possible to build systems rooted in trust, dignity, and human values—while still embracing cutting-edge innovation.
FAQs
Disclaimer: This article is based on publicly available announcements, press releases, and official statements from the Spanish Red Cross and its technology partners. It is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, legal, or technical advice.
#RedCross #BlockchainForGood #DigitalAid #HumanitarianTech #PrivacyFirst#ZeroKnowledgeProofs #Ethereum #AidTransparency #TechForHumanity#Carrerbook#Anslation.